Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is one of the popular network protocols that are used by network engineers to monitor the network traffic and performance. SNMP is a protocol for the application layer, and is an integral part of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Protocol suite. It is identified by the Internet Architecture Board (IAB) for information exchange between network devices. SNMP is an important feature of managed switches, which is configured prior to use. Having said that, you will find this feature on most branded managed switches. VERSITRON is one of the leading manufacturers of managed and unmanaged networking switches in the US. These switches have been an integral part of robust fiber optic networks for several years now. If you are using any of VERSITRON’s managed switches, you may want to know how to configure SNMP on managed switches, isn’t it? If yes, this post leads you through the configuration steps and also provides you insights on SNMP and features.
SNMP and Its Components
Before getting into the steps of configuration, let’s focus on SNMP, its components, and the roles played by these components.
SNMP Agent:
- This is a type of program embedded in the network element. It collects the information from the local device and sends it to the SNMP manager when it requests it. In addition to this, the agent stores and retrieves information from the MIB, as well as signal any event to the SNMP manager. Many times, SNMP agents also serve as a proxy for non-SNMP network modes on the switch. Generally, these agents are standard such as Net-SNMP. Some manufacturers may also provide switches with customized SNMP agents.
SNMP Manager:
- This system communicates with the SNMP agent in the network devices. It is a computer used to manage one or several network management systems. The SNMP manager usually controls the agent. They send regular queries to the agent, receive responses from them, set variables to these agents, and even acknowledge asynchronous events.
Management Information Base (MIB) or Management Information Database:
- Shared between the SNMP Agent and SNMP Manager, this database defines the parameters of the managed device. This database is known as Management Information Database (MIB). The SNMP manager refers this database while sending the query to the SNMP agent. The agent maintains this database to describe the parameters of the managed device. MIB
Managed Devices:
- They are the devices connected to the network, which requires some form of management and monitoring. In this case, networking switches, workstations, routers, and UPS are examples of managed devices.
Steps to Configure SNMP in VERSITRON’s Managed Switches
You can configure SNMP managed switches in web interface by following these steps:
- Click on SNMP system.
- Disable or enable the SNMP function.
- Mention the Engine ID.
- Click on Apply to implement the setting.
Following this, you need to configure trap host, community name, as well as SNMP throttle. To work appropriately, a SNMP manager has to identify community names and pass the authentication. When this happens it can access the target device’s MIB. This means target device and SNMP manager must have the same community name.
Important Parameters for SNMP Configuration in Web Interface
- Mode: This is the operating mode of SNMP. There are two options to choose from – Enabled and Disabled.
- Version: It indicates the version supported by SNMP. There are three options available:
- SNMP v1: Set SNMP supported version 1
- SNMP v2c: Set SNMP supported version 2c
- SNMP v3: Set SNMP supported version 3
- Read and Write Community: This indicates the community access read string that permits access to the SNMP agent. The string length can be anything between 0 and 255. However, this field becomes applicable only for SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c. However, for version SNMPv3, the community string would be associated with the community table of SNMPv3.
- Engine ID: This indicates the engine ID of SNMPv3. The chosen string must contain even numbers with digit length between 10 and 64. However, it may not take all F’s or all zeros. When the engine ID is changed, it will clear all users.
Available Managed and Unmanaged Switches
| SKU | Product Name | Environment | View Details |
| SG70460 | 4-Port Unmanaged Switch | 2-Ports 10/100/1000, 2-1G SFP Slots | Unmanaged | |
| SF70460MP | 4-Port 10/100/1000 Industrial Managed Switch | With 2 PSE PoE+ Ports | 2 100M/1G Fiber SFP Slots | Managed | |
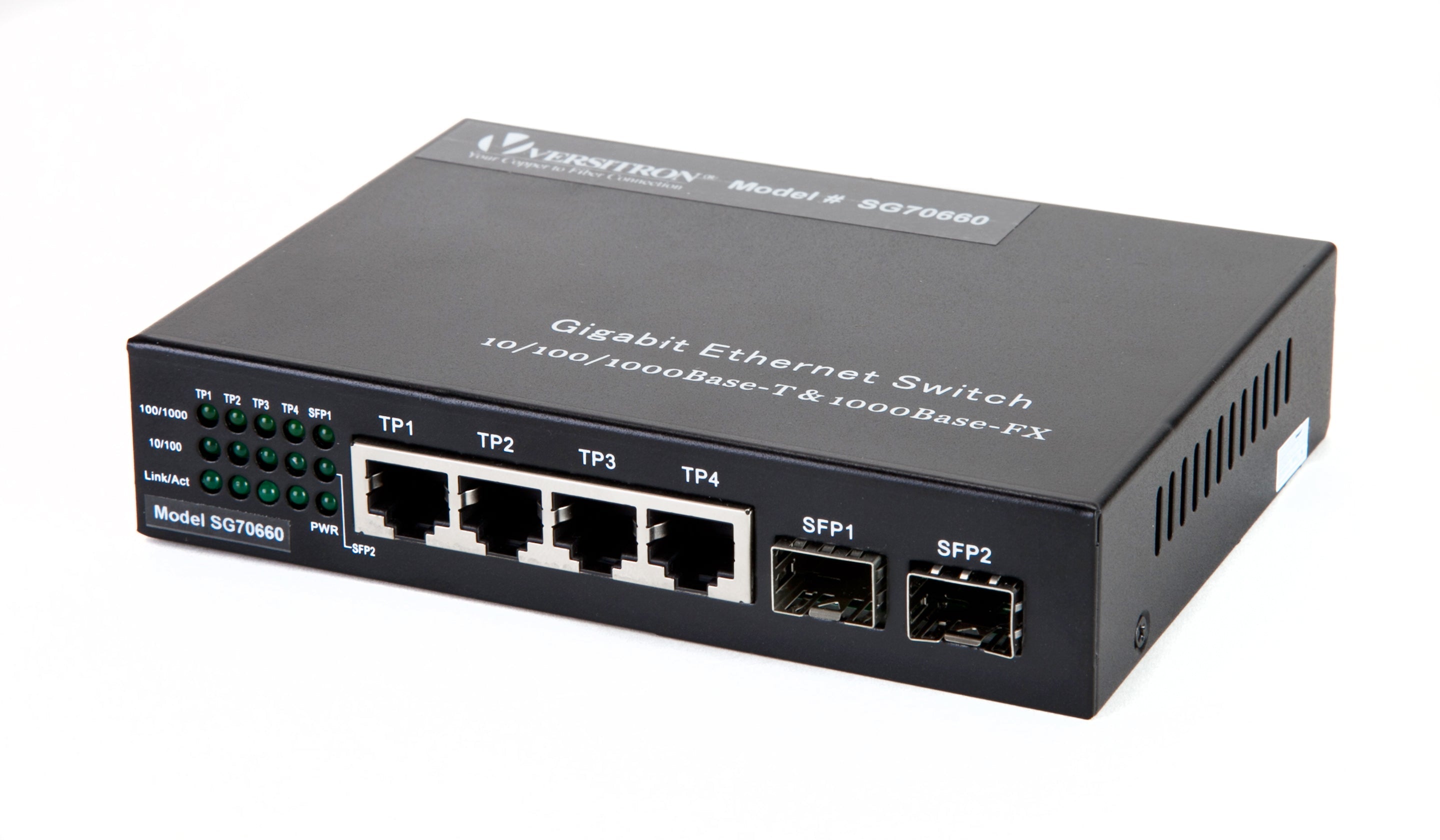
| SG70660M | 6-Port Managed Switch | 5-Ports 10/100/1000, 1-1000 SFP Slot | Managed | |
| SG70660 | 6 Port Gigabit Unmanaged Switch (10/100/1000 mbps, 1G SFP) | Unmanaged | |
| SGX288164M | 28-Port Managed 10/100/1G/10G Layer 2+ “All Fiber” Switch | Managed | |
| SG71090A | Managed Pick a Port 3 Slot Modular Switch With Gigabit SFP Support | Managed | |
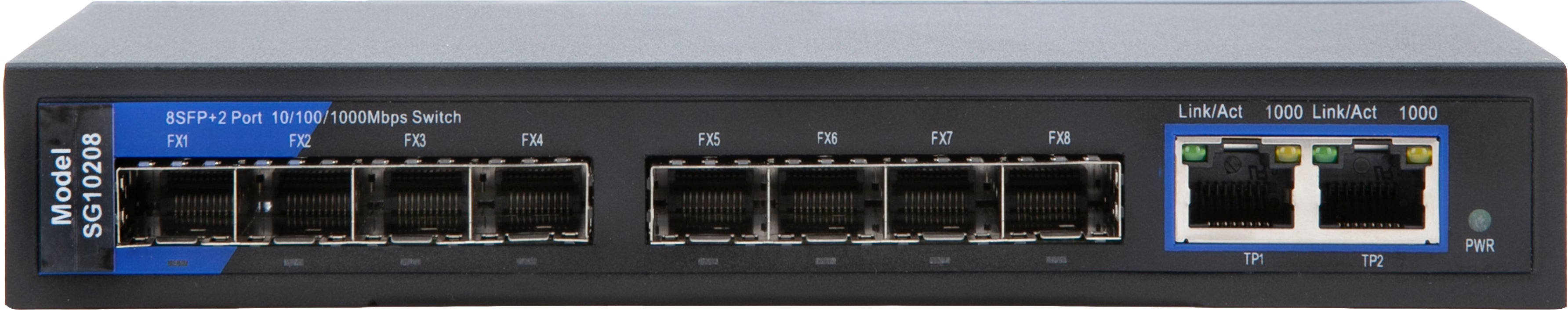
| SG10208 | 10-Port 10/100/1000 Fiber Optic Switch with 8 SFP Slots (1G), 2 10/100/1000 Copper Ports | Unmanaged |