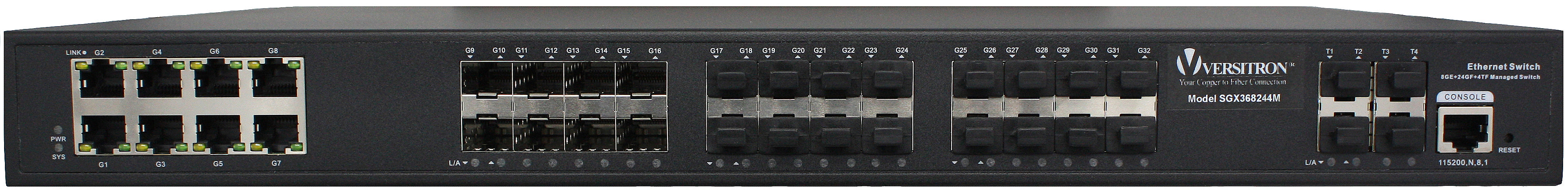
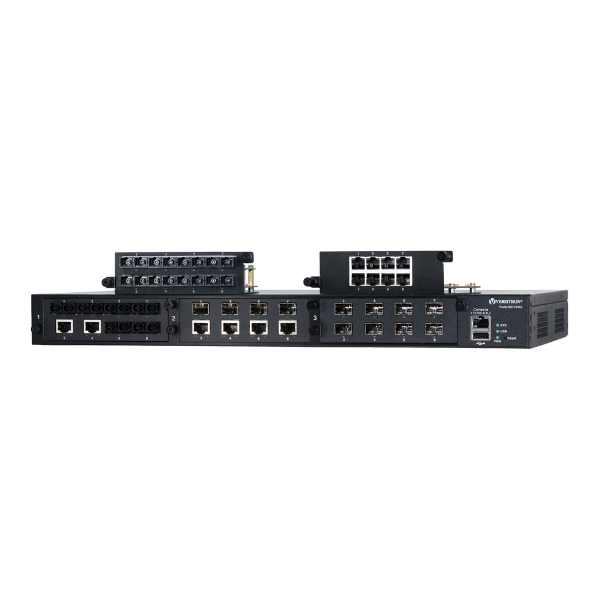
Fiber network infrastructure is the backbone of modern communication and data transfer, enabling faster connectivity and higher bandwidth capacity than traditional copper cables. In this blog, we will discuss the importance of optimizing fiber network infrastructure and explore various techniques to achieve faster connectivity. Faster connectivity and higher bandwidth capacity than traditional copper cables. In this blog, we will discuss the importance of optimizing fiber network infrastructure and explore various techniques to achieve faster connectivity.

What is Fiber Network Infrastructure?
Fiber network infrastructure, also known as fiber optic network infrastructure, refers to the physical framework and components that enable the transmission of data using fiber optic cables. It involves installing and maintaining the necessary equipment and infrastructure to support high-speed data communication.
What is the fastest type of fiber network?
- The fastest type of fiber network currently available is typically based on fiber optic technology using single-mode fiber.
- Single-mode fiber allows for higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to multi-mode fiber.
- It can support speeds up to 100 Gbps or more, depending on the specific technology and equipment used.
What are the components of fiber network infrastructure?
The components of a fiber network infrastructure include:
- Fiber Optic Cables: These cables are made of glass or plastic fibers that transmit data using light signals. They provide high bandwidth and long-distance transmission capabilities.
- Optical Transceivers: These devices convert electrical signals into light signals for transmission over fiber optic cables and vice versa. They are commonly used in switches, routers, and other network devices.
- Optical Switches: These devices allow for the routing of data signals in fiber optic networks. They can switch data between different fiber links, enabling efficient data transmission.
- Fiber Optic Patch Panels: These panels provide termination points for fiber optic cables, allowing for easy connection and disconnection. They help with cable organization and maintenance.
- Optical Splitters: These devices split a single fiber optic cable into multiple fibers, enabling one cable to serve multiple connections.
- Network Equipment: This includes routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and other devices that facilitate data communication and network management.
How does fiber optic infrastructure work?
- Fiber optic infrastructure works by transmitting data as light signals over thin strands of glass or plastic fibers.
- These fibers carry the light signals over long distances with minimal signal degradation.
- The data is converted into light signals using optical transceivers and transmitted through fiber optic cables.
- At the receiving end, the light signals are converted back into electrical signals for data processing.
How to Build Network Infrastructure?
To build a network infrastructure, you can follow these general steps:
- Plan and Design: Determine the requirements of your network, such as the number of devices, data transfer speed, and coverage area. Consider factors like scalability, security, and future growth. Create a network design that includes the layout of cables, network switches, routers, firewalls, and other necessary hardware. Consider factors such as cable routes, connectivity options, and network segmentation.
- Procure Equipment: Purchase the required networking hardware, such as switches, routers, firewalls, servers, and fiber optic cables. Ensure compatibility and quality of the equipment.
- Installation: Physically install the networking hardware, including running fiber optic cables, setting up network switches, and connecting devices. Follow best practices for cable management and ensure proper grounding and power supply.
- Configuration: Configure the network devices according to your design, including IP addressing, routing protocols, security settings, and quality of service (QoS) parameters.
- Testing and Optimization: Conduct thorough testing to ensure connectivity, performance, and security. Optimize the network by fine-tuning configurations, monitoring network traffic, and addressing any issues or bottlenecks.
Techniques to Optimize Fiber Network Infrastructure for Faster Connectivity
Fiber optic networks provide incredibly fast and reliable connectivity, but it's key to optimize the infrastructure to achieve maximum performance.
Here are some techniques for optimizing fiber network infrastructure:
- Upgrade Equipment: Upgrading network equipment such as switches, routers, and optical amplifiers can greatly improve network capacity and data transfer rates. New equipment with higher capacity and faster speeds can handle more traffic and reduce latency. When upgrading equipment, it's important to ensure compatibility with existing infrastructure and plan for future expansion.
- Reducing Signal Interference: Interference can degrade the signal quality of fiber optic cables and impact network performance. To reduce signal interference, fiber optic cables can be shielded from electromagnetic interference and installed in weather-resistant conduits. Additionally, single-mode fibers can be used instead of multi-mode fibers to reduce signal attenuation and improve signal quality.
- Implementing Wavelength Division Multiplexing: Wavelength division multiplexing(WDM) is a technique that allows multiple wavelengths to be transmitted over a single fiber optic cable. This increases network capacity and reduces latency by enabling more data to be transmitted simultaneously. WDM is an effective solution for networks with high bandwidth requirements.
- Network Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular network monitoring and maintenance can help identify and resolve issues such as signal interference, network congestion, and equipment failure. This leads to improved network performance and reduced downtime. Monitoring can also help identify potential issues before they become major problems, allowing for proactive maintenance and upgrades.
Factors Affecting Fiber Network Infrastructure
Fiber optic networks are a reliable and efficient way of transmitting data, but various factors can impact their performance. Understanding these factors can help network administrators optimize the network for faster connectivity.
Here are some critical factors affecting fiber network infrastructure:
- Bandwidth Capacity: The bandwidth capacity of a fiber optic network determines the amount of data transmitted over the network. It depends on factors such as fiber strand number, data transfer rates, and distance. The more fiber strands a network has, the greater its capacity. Higher data transfer rates also increase network bandwidth capacity. Additionally, shorter distances between endpoints improve network bandwidth capacity. Higher bandwidth capacity ensures faster data transfer and connectivity.
- Latency: Latency is the time delay between data transmission and receipt. It is influenced by factors such as network topology, distance, and data transfer protocols. For example, if data travels through multiple nodes or switches, latency increases. Similarly, longer distances between endpoints can increase latency. The choice of data transfer protocols can also affect latency. For instance, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a reliable but slower protocol than User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Reducing latency can improve connectivity speed and quality, resulting in a better user experience.
- Signal interference: Signal interference can affect fiber optic networks' quality and reliability, leading to poor connectivity and data transfer rates. External factors such as weather conditions, electromagnetic interference, and network congestion can cause signal interference. Network congestion can also cause signal interference, leading to slower connectivity and data transfer rates.
- Network Congestion: Network congestion occurs when network traffic exceeds its capacity. It leads to slower connectivity and data transfer rates. Fiber optic networks are designed to handle high traffic volumes, but unexpected spikes can cause congestion. Network congestion can also occur due to inadequate network infrastructure or poor network management. Identifying congestion points and taking appropriate measures to prevent congestion is crucial to optimizing a network. These measures include upgrading infrastructure, implementing traffic management policies, and optimizing the topology of the network.
Future of fiber network infrastructure
Fiber network infrastructure has been rapidly evolving, and its future seems promising. With advancements in fiber optic technology, faster connectivity and higher bandwidth capacity are expected to become the norm. In this section, we will explore some of the key developments that are shaping the future of fiber optic technology.
- Advancements in Fiber Optic Technology: Fiber optic technology is advancing at a breakneck pace, with new innovations emerging in cable design, signal processing, and network architecture. One such innovation is the development of multicore fibers, which can carry multiple streams of data simultaneously, thereby increasing the bandwidth capacity of the network. Researchers are also exploring ways to reduce the loss of signal strength, which can occur during data transmission over long distances. This is being achieved through the use of advanced signal processing techniques that can compensate for signal loss and improve network performance.
- Impact on Connectivity and Speed: The future of fiber optic technology looks bright, with faster connectivity and data transfer rates becoming a reality. With higher bandwidth capacity, it will be possible to transmit large amounts of data in real-time, enabling seamless communication, streaming, and gaming. This will also open up new avenues for businesses, allowing them to leverage the power of big data to make more informed decisions and gain a competitive edge.
- Potential applications: Fiber optic technology has vast potential applications across various industries, including telecommunication networks, healthcare, transportation, and smart cities. For instance, in healthcare, fiber optic networks can be used to transmit medical data and images in real-time, enabling remote diagnosis and treatment. In transportation, fiber optic networks can be used to improve traffic management, reduce accidents, and enhance communication between vehicles. In smart cities, fiber optic networks can be used to enable efficient and sustainable infrastructure, such as smart lighting, waste management, and energy management systems.
Conclusion:
Efficient fiber network infrastructure is imperative for achieving faster connectivity and enhancing network performance. Upgrading equipment, minimizing signal interference, and deploying WDM are some of the techniques that can aid in achieving this objective. Versitron Ethernet Network Switches, known for their robustness, high-speed data transfer, and reliability, are an excellent option for optimizing fiber network infrastructure. With continued advancements in fiber optic technology, we can expect even faster connectivity, increased bandwidth capacity, and innovative applications in diverse industries. Investing in and optimizing fiber network infrastructure is essential as we progress towards a digital future, facilitating better communication and connectivity.