Voice over IP, which is popularly known by its abbreviation VoIP, has been around for several years now. Many organizations and businesses have already switched from the earlier public switched telephone network (PSTN) to VoIP, a much-advanced telecommunication technology. PSTN is a comprehensive term for all switched telephone networks that are being operated by national, local, and international carriers. It is alternatively known as plain old telephone service (POTS). These networks deliver the services and infrastructure required for a phone conversation. Against a PSTN, VoIP utilizes internet technology to deliver voice calls. Are you intrigued to know more about this technology? This post answers all questions that you may have regarding VoIP.

What is VoIP? What Are its Similarities and Differences with Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS)?
VoIP enables you to make voice calls over the Internet connection rather than an analog phone connection. VoIP solutions require no hardware, unlike the traditional POTS phones. As known, the analog phones are supported by telephone companies, whereas VoIP phones are supported by VoIP providers, which transmit your call through a high-speed Internet connection.
Although technologies and infrastructure differ across VoIP and PSTN, their basic functions remain the same. For instance, you still have to take a phone and dial a number. The recipient also receives the phone in the same manner as earlier. Many features that existed in PSTN also exist here. These include putting a call on hold, voicemail, routing calls to an alternate number, and IVR systems. Many VoIP systems also support faxing.
How VoIP works?
If you are using a regular telephone, the signal is converted into an analog signal before it is delivered to the recipient. The analog phone uses circuit switching technology to support a call. The circuits are opened by the caller who calls the recipient. These circuits remain open throughout the call and no other calls can travel the same route. This is why long-distance calls are usually expensive.
The working of voice over internet protocol is slightly different. VoIP technology enables you to make a call from your computer using a VoIP phone or an analog phone that is connected to a special adapter. Your voice is routed over data networks such as the internal enterprise LAN or the Internet. VoIP mainly uses packet switching technology that converts the human voice into data packets. These data packets are delivered to intended recipients. These data packets use different routes for transmission. Once delivered, they are automatically assembled in the right order and transformed into a sound signal. The VoIP also supports wireless technologies. These wireless VoIP phones are commonly used at locations such as cafes, parks, airports, and other public places.
What Are the Technical Requirements of a VoIP System?
A high-speed Internet or a broadband connection is a necessity for a VoIP system, along with a specialized phone, an adapter, and a computer. The broadband connection can be made through a high-speed services DSL, a cable modem, or a LAN. Some VoIP services may require a computer, and some may require a special phone. A few of them also support traditional phones connected to a VoIP adapter. If you are using the traditional phone, perhaps, you can dial like a regular phone and you can hear a dialer tone, too. If you are using a computer, you would need supporting software and a microphone to make a call. Some advanced VoIP phones can be directly plugged into broadband.
What Are the Advantages of VoIP?
Over the years, VoIP systems have gained immense popularity over traditional systems owing to several benefits they offer. The following points will help you understand it better:
- Simple Set-up and Requires No Major Investment: VoIP is offered as a hosted solution, thus, the set up becomes easy. It requires no additional investment in terms of equipment and devices. Businesses can use their existing desktop computer, tablet, or smartphone. Also, if they are using a traditional analog phone, it can be easily converted into a VoIP phone using an adapter. The set up can be easily completed within a few hours.
- Supports Data and All Forms of Digital Communication: Remote team collaboration has become a necessity in today’s world. This is supported by VoIP phones. Hosted VoIP solutions support interoperability. They help connect calls to the same network as instant messaging, group file sharing, group chats, video sharing, conference calls, teleconferencing, and so on.
- Free Phone Calls or Affordable Rates Assured: Some VoIP services support free calls made to subscribers using the same services. However, some VoIP services would charge you for calls made outside your area of calling, while others may allow you to call anywhere for a fixed number of minutes. These calls are charged at flat rates.
- Supports Mobility: VoIP phones support mobility as they support cloud architecture. Business VoIP is not connected to any particular location and you can access it even if you are relocated to a new premise. This makes business communication a lot easier.
- Supports Several Business Features: Cost reduction is one of the biggest advantages of using VoIP phones. They support unlimited faxing and calling, which can be a boon for businesses that operate as exclusively sales-only operations. These phones use only the necessary amount of data to make a call, thus, allowing you to save on data. Many VoIP packages also support features such as Auto Attendant, Unified Communications, Video Conferencing, HD Voice Quality, IM& Chat, and so on.
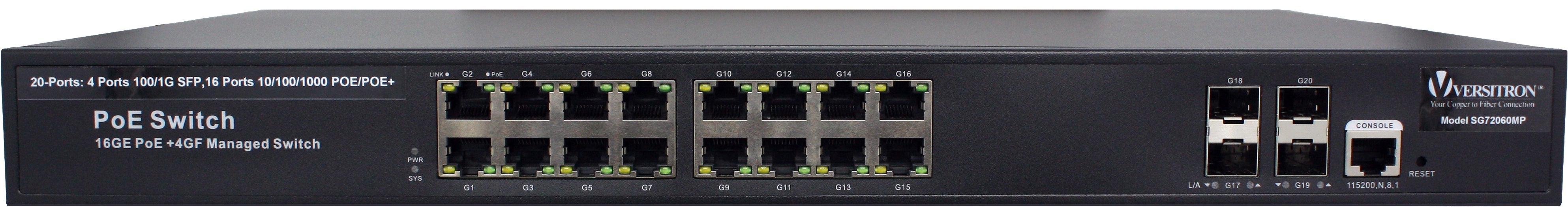
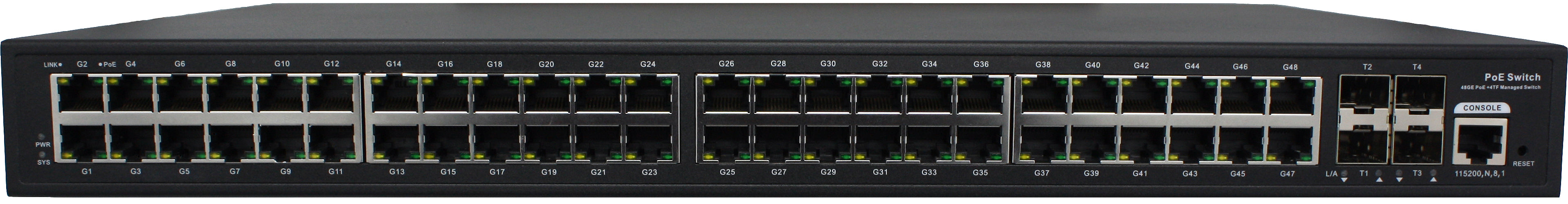
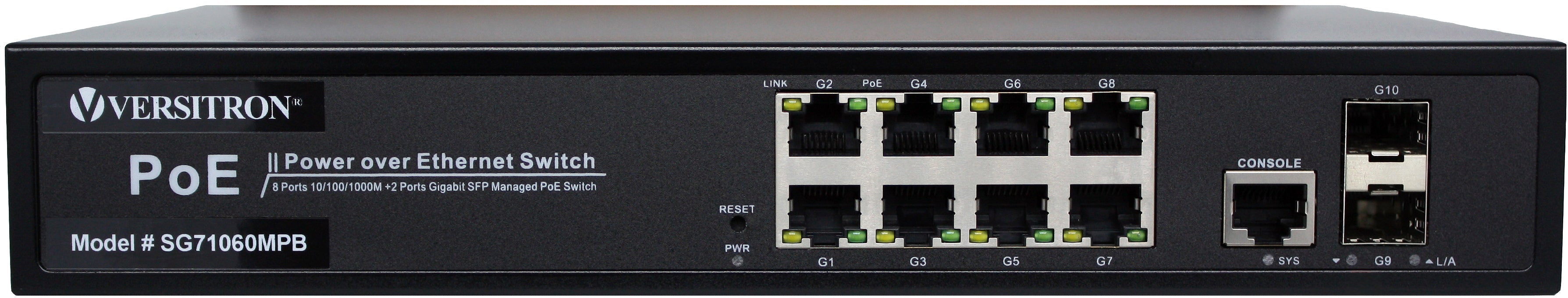
As the benefits of VoIP are introduced here, it is important that you source adapters, converters, and other accessories from a trusted manufacturer. Versitron provides PoE media converters with fiber and PoE switches, POTS which are required for making stable VoIP connections.